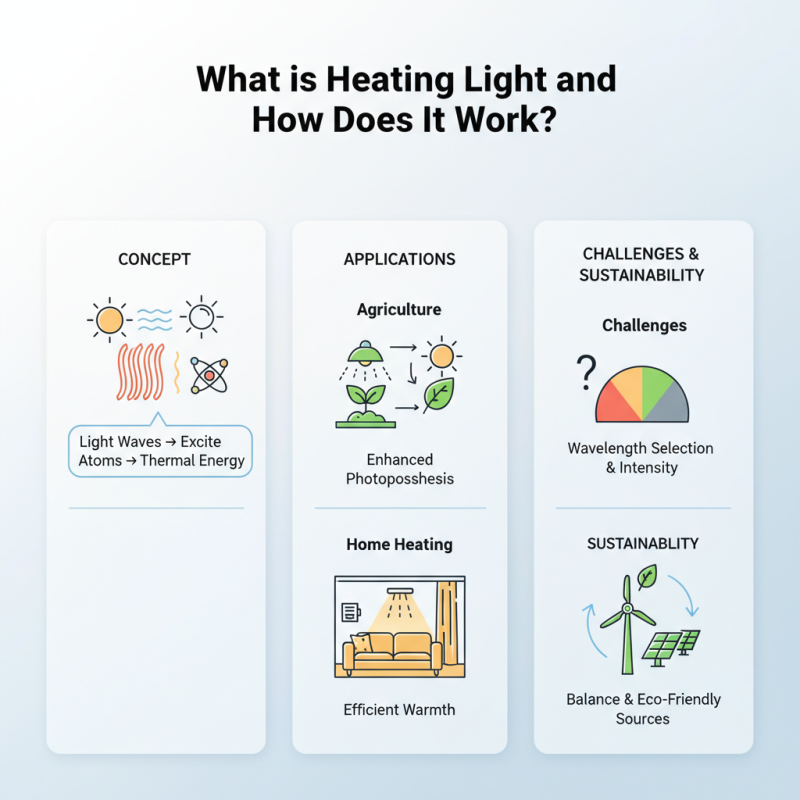
Heating light is a fascinating concept in the realm of thermal energy. It refers to the effective use of light waves to generate heat, transferring warmth to various materials and environments. This process relies on specific wavelengths of light to excite atoms, creating thermal energy.
Understanding heating light is essential in many applications. From agriculture to home heating, its potential is vast. Plants absorb specific light frequencies, promoting growth through enhanced photosynthesis. In homes, heating light can provide warmth and comfort efficiently, reducing the need for traditional heating methods.
However, there are challenges to consider. The intensity and type of light can impact effectiveness. Not all wavelengths may be suitable for specific tasks, making careful selection vital. Additionally, the environmental impact of generating heating light warrants reflection. Striking a balance between effective use and sustainability is crucial for future innovations in this field.
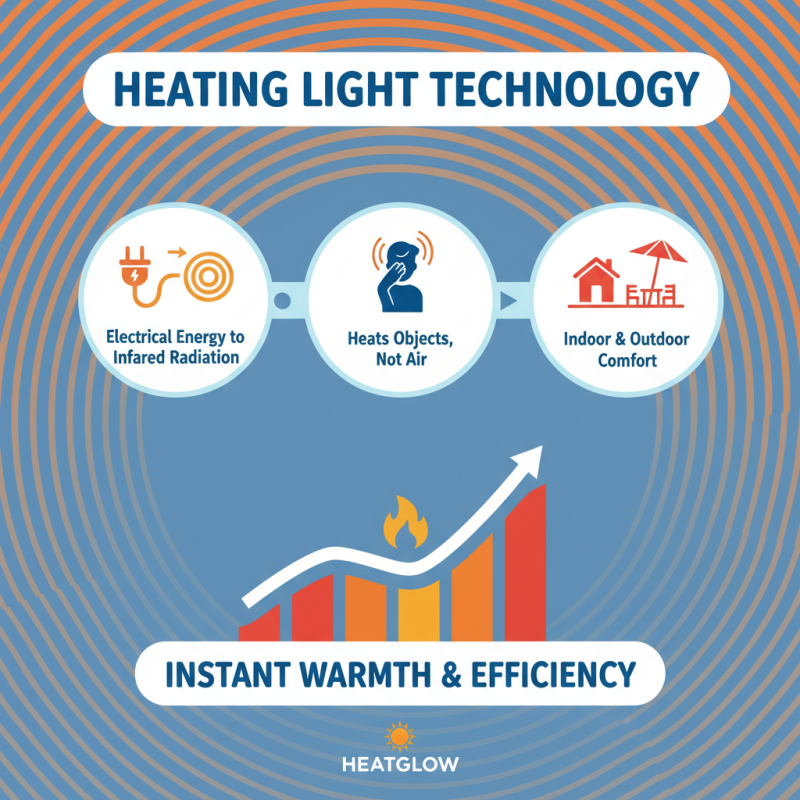
Heating light is a fascinating technology that generates warmth and comfort. It operates by converting electrical energy into infrared radiation. This radiation heats objects in its path rather than the air. This means you can feel the warmth without making the entire room hot. It's suitable for both indoor and outdoor spaces.
In application, heating lights are often used in restaurants, porches, and even bathrooms. They provide immediate warmth and create cozy environments. However, they can be somewhat inefficient in larger areas. It's essential to consider placement carefully. The right positioning can maximize heat while minimizing energy waste.
Tips: Use heating lights in small spaces for the best results. A well-placed light can warm you efficiently. Always read instructions to ensure safe usage. Assess whether your heating light is truly necessary before installation. Sometimes, natural sunlight or other heating methods might be a better option.
Heating light technology relies on the principles of infrared radiation. This type of light emits energy that creates heat. When it hits an object, the energy is absorbed and transformed into warmth. This process is common in many heating solutions.
Understanding the science behind heating light reveals its efficiency. Infrared waves have longer wavelengths than visible light. This allows them to penetrate materials better and distribute heat evenly. Many people use heating lights for instant warmth in their homes. However, it’s essential to consider placement. Positioning is crucial for optimal effectiveness.
Despite its many benefits, there are challenges. Not every space is suited for heating light technology. Incorrect usage can lead to uneven heating or energy waste. Users often overlook safety guidelines. Maintaining a safe distance from flammable materials is vital. These aspects require careful thought and planning for successful implementation.
Heating light technology finds diverse applications across various industries. One primary application is in agriculture. These lights are used to warm greenhouses, ensuring optimal growing conditions year-round. Reports show that the controlled environment can enhance plant growth by up to 30%. Farmers can manage temperature and humidity effectively, leading to higher yields. However, the cost of energy remains a concern, and many are seeking more sustainable options.
In the field of healthcare, heating lights play a crucial role in therapy. They can alleviate pain and reduce muscle tension. According to recent studies, patients using heat therapies report a 25% improvement in comfort levels. However, the accessibility of such treatments varies widely. Some clinics may lack adequate facilities, leaving patients with limited options. This gap raises questions about equitable access to effective therapies.
Moreover, industrial applications also benefit from heating lights. Factories use them for curing processes and maintaining temperature-sensitive machinery. Data indicates that proper heating can reduce production defects by 15%. Yet, there are challenges. The initial setup costs can be substantial, and ongoing maintenance is necessary to ensure efficiency. Industries must weigh these costs against the benefits of improved production quality.
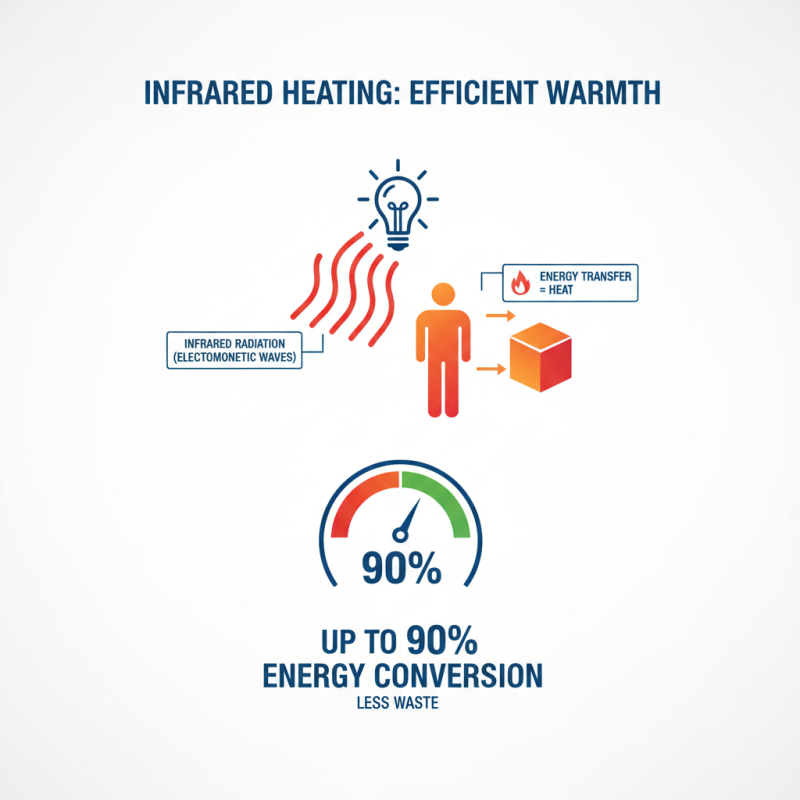
Heating light plays a crucial role in generating warmth. It utilizes infrared radiation, a type of electromagnetic radiation. When these waves hit an object, they transfer energy, creating heat. The efficiency of heating lights can be quite impressive. According to recent industry reports, they can achieve up to 90% energy conversion into heat. This means less energy is wasted during the process.
The design of heating lights often allows for direct heat application. This creates immediate warmth in targeted areas. For example, in an industrial setting, heating lights can be used for curing processes. They help in drying paints or inks quickly. However, coverage can sometimes be uneven. Some spots might receive excessive heat, causing potential damage.
Consumers often complain about the initial cost of heating lights. While they offer long-term savings on energy bills, the upfront investment can be daunting. A report found that installation costs may deter some users. This highlights a gap in affordability. Balancing efficiency and cost is essential for broader adoption.
Heating light, a type of infrared light, has become popular in various fields. It is often used in
agriculture, animal husbandry, and even in heating small spaces.
The primary advantage of heating light is its efficiency. It quickly warms objects and surfaces without heating the air. This feature is
especially useful in cold environments. Many people appreciate how it can provide targeted warmth.
However, heating light has its drawbacks. Prolonged exposure can harm sensitive skin or eyes. The heat may also be uneven,
leading to hot and cold spots. In some cases, users notice a significant increase in energy consumption.
These limitations raise questions about cost-effectiveness. It is crucial to assess the benefits against potential risks.
People need to reflect on whether the advantages outweigh these concerns in their specific situations.





